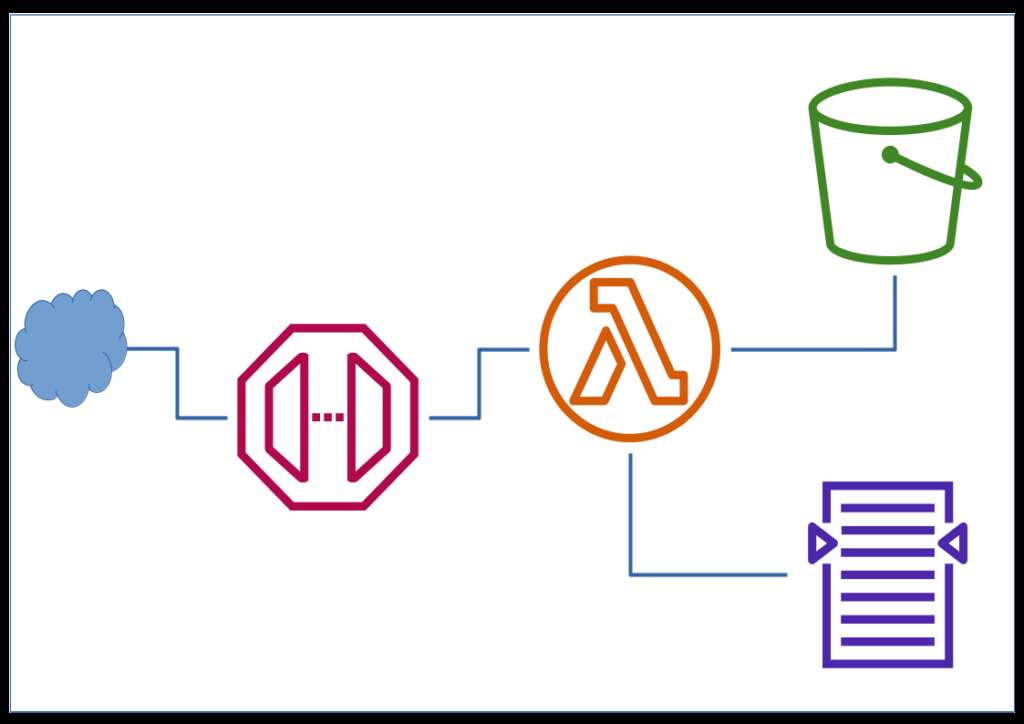
The choice between OpenShift on-premises, Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), and Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA) is a critical decision for organizations seeking to leverage the power of Kubernetes. This article delves into the key differences and advantages of these platforms.
Understanding the Contenders
- OpenShift on-Premises: This is a self-managed Kubernetes platform that provides a comprehensive set of tools for building, deploying, and managing containerized applications on-premises infrastructure.
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS): A fully managed Kubernetes service that allows users to run and scale Kubernetes applications without managing Kubernetes control plane or worker nodes.
- Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA): A fully managed OpenShift service on AWS, combining the strengths of OpenShift and AWS for a seamless cloud-native experience.
Core Differences

Advantages of AWS Offerings
While OpenShift on-premises offers granular control, AWS EKS and ROSA provide significant advantages in terms of scalability, cost-efficiency, and time-to-market.
Scalability and Flexibility
- Elastic scaling: EKS and ROSA effortlessly scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
- Global reach: AWS offers a vast global infrastructure, allowing for seamless deployment and management of applications across multiple regions.
- Hybrid and multi-cloud capabilities: Both EKS and ROSA support hybrid and multi-cloud environments, enabling organizations to leverage the best of both worlds.
Cost-Efficiency
- Pay-as-you-go pricing: EKS and ROSA eliminate the need for upfront infrastructure investments, allowing organizations to optimize costs based on usage.
- Cost optimization tools: AWS provides a suite of tools to help manage and reduce cloud spending.
- Spot instances: EKS supports spot instances, offering significant cost savings for non-critical workloads.
Time-to-Market
- Faster deployment: EKS and ROSA provide pre-configured environments and automated provisioning, accelerating application deployment.
- Focus on application development: By offloading infrastructure management, teams can concentrate on building and innovating.
- Continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD): AWS offers robust CI/CD tools and services that integrate seamlessly with EKS and ROSA.
Security and Compliance
- Robust security: AWS is known for its strong security posture, offering a comprehensive set of security features and compliance certifications.
- Regular updates: EKS and ROSA benefit from automatic updates and patches, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities.
- Compliance frameworks: Both platforms support various compliance frameworks, such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOC 2.
Conclusion
While OpenShift on-premises offers control and customization, AWS EKS and ROSA provide compelling advantages in terms of scalability, cost-efficiency, time-to-market, and security. By leveraging the power of the AWS cloud, organizations can accelerate their digital transformation and focus on delivering innovative applications.
Note: This article provides a general overview and may not cover all aspects of the platforms. It is essential to conduct a thorough evaluation based on specific organizational requirements and constraints.